[ad_1]
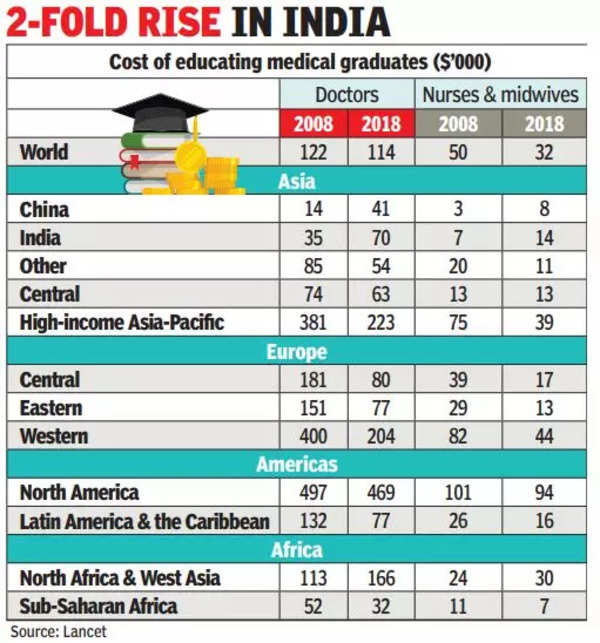
The pattern was the same for nurses with the estimated expenditure per nursing graduate dropping across the world while it went up by 167% in China and doubled in India. The only other region where the per graduate cost went up was in North Africa, where cost per doctor went up by 47% and by 25% for nurses.
Approximately $110 billion was invested globally by governments and students’ families in medical and nursing education in 2018. Of this, $60.9 billion was invested in doctors and $48.8 billion was invested in nurses and midwives, the study estimated.
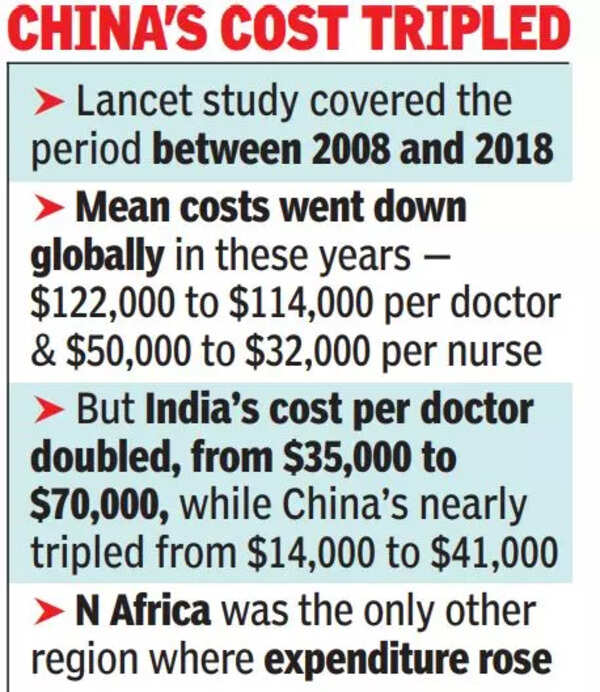
The paper looks at important developments in medical education to assess potential progress and issues with education of health professionals after the Covid-19 pandemic. Mean costs in 2018 were $114,000 per doctor and $32,000 per nurse. In 2008, China had the lowest estimated expenditure per medical graduate at just $14,000 (Rs 6 lakh) followed by India, where it was just $35,000 (Rs 15 lakh at the 2008 exchange rate of Rs 43 to a dollar). This is much lower than the estimate of Rs 1 crore or more that Indian colleges widely claim as expenditure per medical graduate.
The expense reduced most dramatically in Europe, where it halved across all European regions between 2008 and 2018. It fell by almost 42% in Latin America too. Per capita expenditures for training doctors and nurses were ten times more in North America than in Sub-Saharan Africa.
The money spent on educating doctors and nurses was highest in North America ($21.4 billion), followed by western Europe ($8 billion). Globally, 56% of medical schools were public and 39% were private. However, the increase in the number of private schools was more than the increase in the number of public schools, showing that not enough public financing was happening to fulfil the demand for healthcare workers.
Increases in graduate numbers were more substantial in high-income countries than in low-income countries, and in private schools than in public schools. “Despite having a higher density of healthcare workers and more professionals graduating than low-income countries, high-income countries (and high-income regions within countries) continue to attract and retain professionals from low-income countries and regions,” noted the study.
According to the paper, globally, the annual number of medical and nursing graduates has almost doubled for doctors and tripled for nurses and midwives over the 10-year period. This is much higher than the global population growth of just 8%, thus nearly doubling doctor-population ratios. Nurses, unsurprisingly, are the majority (59%) of health professionals — more than all other professional groups combined.
[ad_2]
Source link